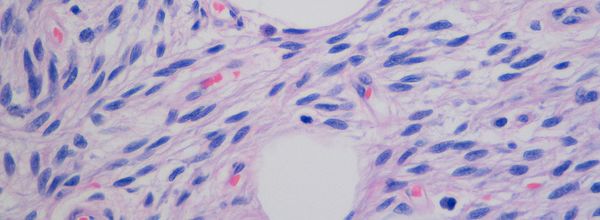
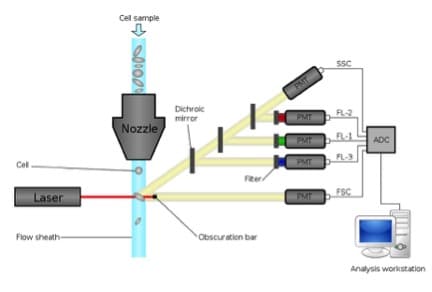
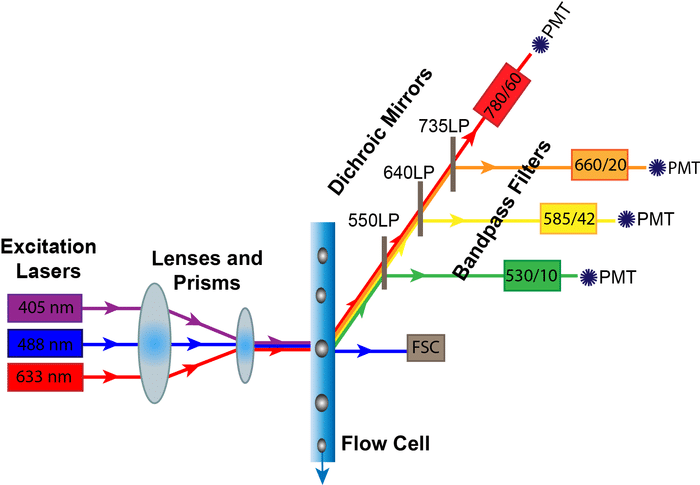
How Fluorescent Molecules Work
Nearly every field, from physiology to immunology, uses fluorescent molecules to detect or measure something. This article explains how fluorescent molecules work for biologists—without all the complicated photochemistry.