Beginners Guide to PALM Sample Preparation
Good PALM sample preparation is the key to great images. Find out how to choose the right fluorescent proteins and learn some tips and tricks for sample prep.
Join Us
Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.

Good PALM sample preparation is the key to great images. Find out how to choose the right fluorescent proteins and learn some tips and tricks for sample prep.

Want to build your own microscope for almost nothing? You probably already have most of the tools that you need right in your lab or at home! Here’s how.

Can lasers be used to trap and move objects? Sure they can! Read on to know how you can use lasers in a cool technique called optical tweezers to manipulate minuscule objects under the microscope.

Don’t get overexcited but we’ve got 7 top tips to help you minimize photodamage during your fluorescent live-cell imaging experiments.

Tips on staying sane from a student survivor of tedious lab tasks.

Discover how structured illumination microscopy works can help you see things in greater detail.

Stop wasting time throwing out slide after slide trying to create a readable blood smear. Read our how-to guide for creating the perfect blood smear slide.

The electron microscope (EM) – where electrons, rather than photons, make the image – fell out of fashion for a while, but it has come back refreshed. Modern electron microscopes cost less, use less electricity, and are generally easier to maintain than the older models, so it is likely that you can get your hands on one. Read on to learn more about this technique, and how to implement it into your research.

Shared microscopes have the potential to get dirty and spread nasties between samples and users. Check out our quick guide on how to clean and disinfect your microscope.

Don’t be daunted by imaging and analyzing your wound healing assay; our top tips will get it looking perfect.

Wound healing assay is one of the earliest and simplest in-vitro assays for studying cell migration. Discover if this assay is right for you and learn how to set it up to get reproducible data.

Sample fixation for electron microscopy can be done using either chemical fixation or cryofixation. Discover the benefits and drawbacks of each of these methods.

Ultramicrotomy is the process by which a sample is cut into very thin slices or “sections”, usually for imaging by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) or relatively new techniques using scanning electron microscopy (See Array tomography in three-dimensional scanning electron microscopy for biology). This technique requires a bit of finesse, and this article will help you…

Have you ever been looking through a box of slides and found something that you want to image or look at later, or even show to one of your colleagues or supervisor? Finding that exact spot on the slide at a later date can prove to be difficult- using a marker pen on the coverslip…
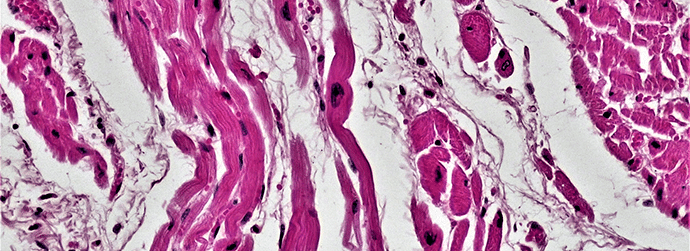
What Is Optical Mapping and How Is It Used? Synchronisation of the contraction of heart muscle is essential for the efficient pumping of blood through the circulatory system. Cardiac contraction is controlled by the regulated spread of electrical impulses from cell-to-cell within the heart. In pathological conditions, these electrical impulses can become disordered and lead…

RNAscope is a new method of quantitative RNA in situ-hybridization that has taken laboratories by storm. Learn advantages over traditional techniques and how RNAscope works in this introduction article.

Automated image analysis uses finely tuned software to extract data from digital images. Algorithms recognize specific shapes and patterns in the images and gather quantitative information that is then used for further data analysis. The pharmaceutical and biological research industries have benefitted greatly from this technology, which allows researchers to analyze hundreds—if not thousands—of samples…
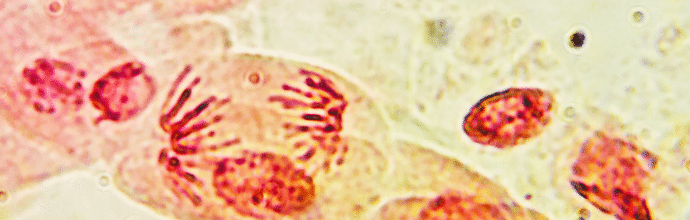
As an undergraduate student, one of the first experiments I did was staining chromosomes in mitotically active onion root tip cells. The stains that are conventionally used for this purpose are acetocarmine or aceto-orcein (which smell like vinegar). However, the cost of these stains is quite high. Personally, I find safranin, which is another stain, more…
Ever since the invention of the first compound microscope by Zacharias Jansen in 1590, our understanding of the microscopic world has grown exponentially. Microscopes have evolved from mere assemblies of magnifying lenses to extremely powerful tools for visualization on the atomic scale. You can find a wealth of information on the workings of a microscope…

There are two types of electron microscopy—transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). SEM creates fascinating 2D images by bouncing electrons off the surface of the sample. I highly recommend searching for SEM samples on Google images. There are a wide variety of applications for electron microscopy. While SEM images are aesthetically amazing,…
Immunolabeling is the tried-and-true immunochemistry method of getting the stain you want onto the molecular target you want. Whether that target is contained within a large region of tissue (immunohistochemistry) or inside a single cell (immunocytochemistry), the ability to accurately label large numbers of samples will simplify your workflow and help you to achieve excellent…

Continuing from our first article on lasers for confocal microscopy, we will now discuss two specialized types of lasers: lasers for two-photon excitation and tunable, white light lasers. We will also discuss the applications of the two lasers. Lasers for Two-Photon Excitation The two-photon absorption phenomenon was first described for microscopy in 1931. Here, the…

In the first part of this series, we discussed the differences between a color and a monochrome microscope camera and when one is advantageous over the other. We also touched on the subject of optimal camera resolution for a given imaging system. In this part, we will tackle a few additional camera specifications and how…

From Alkaline phosphatase to Warthin-Starry, we take you through the various histology stains available.

Purchasing a microscope camera is one of the most daunting tasks you might have to undertake. Before you set out to buy that camera, carefully consider your applications. Things like sample brightness or the speed of the phenomenon you are trying to capture can dictate your choices. Also, this is the time to make peace…
Interested in the detailed structure of your tissue? High-resolution imaging techniques, such as brain electron microscopy, provide an intricate view of your tissue. While it may be a rather complicated procedure with nasty chemicals, the advantages of epon embedding can make it the best choice for morphological studies. The hard blocks are excellent for structural…

Tissue embedding and sectioning is a backbone of many biological research labs. While commiserating with other grad students over tedious hours spent in the lab, you’re probably aware that there is more than one way to slice up a chunk of tissue. We’ve previously introduced what to consider when choosing a tissue embedding medium and…
Are you trying to figure out how to calculate intensities of fluorescently-labeled single cells? Do you have cells at high densities or present in clusters? Are you worried that your current cell imaging analysis software is unable to mark clear boundaries around each cell in a cell cluster? Don’t fear, because CellProfiler 2.1 is here to…

If you want the kind of fluorescent IHC images worth those extra color publication charges, you’ve come to the right place. Read on for tips and tricks to getting stellar IHC staining.
Unpacking the Daunting Task of Stereology for Electron Microscopy Electron microscopy provides fantastic detail and resolution, with brain electron microscopy allowing visualisation of neurons and their individual synaptic connections. You may find yourself needing to count these neurons or connections, which can easily go into the billions. But counting these one-by-one isn’t really feasible. This…

Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, can be detected on tissue slides using stains in conjunction with immunohistochemistry and/or reporter assays.
The traditional microscope that you know and love is operated manually. Picture the scene: the microscopist chooses the light source, gently places the sample the moveable stage, selects the objective lens, and scans to select the field of view. This process is perfect for processing and analyzing a small number of samples per day.But nowadays,…

Discover a way to study the active form of proteases in situ with in situ zymography. Read this article to get up to speed.
Cell counting is the bane of existence of many researchers. Countless hours spent in front of the microscope with a haemocytometer on the stand and a manual tally (or “clicker”) in hand can be really daunting. Not to mention that no one will ever double check your count if you don’t take a picture. Those…

A routine task in the lab is to investigate the presence of your favorite protein in a range of histological samples. No doubt, staining your tissue sections using good old immunohistochemistry (IHC) would be your first choice. You just got to love a technique that has celebrated its 70th birthday, and is still used in…
Techniques to study entire tissues, such as brain imaging microscopy, provide great insight into the biology of the whole tissue, rather than just individual cells. Taking this one step further is intravital microscopy (IVM); a newer approach for the imaging of living tissues and organs in live animals. A wide variety of organs can be…
In recent years, three-dimensional (3D) scanning electron microscopy techniques have gained recognition in the biological sciences. In particular, array tomography, serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBFSEM) and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIBSEM) (described in Three-Dimensional Scanning Electron Microscopy for Biology) have shown an increase in biological applications, elucidating ultrastructural details of cells…

Cryosectioning is difficult when your tissues melt, fold, curl, wrinkle, tear, or crack. Learn how to troubleshoot these pesky cryosectioning problems.

While the microscope is synonymous with biology, it is a child of physics and technology. When we learn about the microscope we learn physics—specifically, we learn about optics. Many great resources are available that explain the inner working of microscopy. And, like most things in physics, the inner working of microscopes comes down to a numbers…

There are those of us who began our careers literally in the dark. Yes, there was a time and not that long ago, that all figures had to be on film. Slide presentations were slides. Micrographs were, well, micrographs on film. Figure creation involved several steps: figures for publications had to be mocked up; then…

The eBook with top tips from our Researcher community.