Getting Started with NGS Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics and NGS go together like peanut butter and jelly. But if you’re just starting out with these techniques it can be daunting.
Join Us
Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.

Bioinformatics and NGS go together like peanut butter and jelly. But if you’re just starting out with these techniques it can be daunting.

The success of whole genome sequencing (WGS) is shown in the quick and efficient scientific response to the 2011 outbreak of E. coli in Germany and France.1 German and French strains of E. coli were indistinguishable using standard tests. However, WGS analysis showed 2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the German strains and 9 SNPs…

The advent of Next Gen Sequencing (NGS) has been truly amazing. One of the marvels that is often overlooked is how advances in DNA extraction technology have helped streamline NGS workflows. The original standard – phenol/chloroform extraction – is not well suited to the automated nature of today’s sequencing workflows (though with the emergence of…

Nanopore is a relatively new sequencing platform and researchers are still trying to optimize the protocol for their own specific applications. In our lab, we work primarily with metagenomic samples and use the 1D sequencing kits. Over the past year, we have optimized this technique. To check the quality of the Nanopore library preparation we…
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has ushered in a new era of understanding of both the inner workings and the function of the genome. NGS allows researchers to look at traits—including diseases—that are linked to differences or mutations in an individual’s genes. Since only about 1% of the human genome constitutes genes that code for proteins, several…

One of the most powerful methods of modern cellular biology is creating and analyzing RNA libraries via RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq). This technique, also called whole transcriptome shotgun sequencing, gives you a snapshot of the transcriptome in question, and can be used to examine alternatively spliced transcripts, post-transcriptional modifications, and changes in gene expression, amongst other applications….

The epigenome has been in the research spotlight, and for good reason. Not only has it been associated with the developmental stages of an organism, but epigenetic alterations lead to disorders and have been linked to many human diseases. So, the question stands: what exactly is an epigenome? What Is the Epigenome? Simply put, the…

Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, better known as ChIP-seq, is a massively parallel approach for understanding the interactions between proteins and DNA. This is especially important for determining the activity of transcription factors, which is why it’s frequently used to learn about the complicated series of biological steps leading to cancer. It’s also key to many epigenetic…
Construction of high-quality sequencing libraries is pivotal to successful NGS, and DNA quality is one of the most critical aspects of library preparation. As this Nature Methods paper illustrates, DNA shearing involves appropriate and consistent fragment sizes for sensitive and accurate sequencing, and the fragments must be accurately analyzed prior to sequencing to measure molarity…
DNA sequencing is the most powerful method to reveal genetic variations at the molecular level, leading to a better understanding of our body in physiological settings, and pathological conditions. It is the beginning of the long road towards better diagnostics and personalized medicine. Even though there have been great advances in DNA sequencing technologies there…

Used for matching organ transplants to donors and other applications, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing is rapidly shifting from older methods to NGS technologies. This is a major step forward, as more complete views of the highly polymorphic HLA genes provide a deeper understanding of how a person’s natural genetic variation might affect transplant matches…

NGS is not a three-headed monster. However, it can be a difficult concept to grasp—especially when you are getting started. There is a lot of new terminology, and a whole new world to discover: both in the lab bench and in interpreting your results. It helps to start somewhere. So, let’s start! Depth of Coverage…
SNPs or single nucleotide polymorphisms are on many scientist’s wish list in experimental studies of genomic DNA sequences. Methods to detect SNPs have evolved. Now with the availability of high throughput sequencing methods, also known as next generation sequencing (NGS), SNPs can be identified in the large amounts of DNA sequence that is generated. There…
Anytime lab processes get automated by a sophisticated scientific instrument, there can be a “black box” effect, leading users to wonder what’s going on in there. For DNA electrophoresis, it’s no different. It’s easy to see what’s happening in a manual gel, but the automated gel-based DNA size selection platforms can be more mysterious. Automated…

It’s the hot new technique. With a single procedure, you can get information about all RNA transcripts at once! It sounds like a dream. While RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) has opened the door to exciting new questions, scientists interested in pursuing this technique should be aware of the roadblocks ahead of them. While RNA-seq can be…
Scientists today depend heavily on many molecular biology techniques to perform their research. For example, with the advent of next generation sequencing (NGS): scientists are able to look at very minute details, right down to individual genetic sequence variations. However, the increase in experimental complexity means that every extra step becomes more crucial than…

The ability for DNA polymerase to copy a long stretch of DNA is becoming increasingly important. Why? It has to do with the advances in our sequencing technologies. Our next generation sequencing (NGS) technology requires the DNA polymerase to copy a long stretch of DNA (sometimes up to 50kb) as NGS is churning out genetic…

Now you’ve got great sequencing results, thanks to Nick’s article on improving sequencing results. Now what? Well now you need some software (preferably free) to analyze your data. BioEdit is a good option. But what I have to offer today is a much lighter and equally handy tool. It’s called Artemis and was developed by…
Recently, I have witnessed the uprising of various next generation sequencing (NGS) platforms and it’s quite interesting because each platform uses a different method. Previously, I’ve written about the exciting possibility of nanopore sequencing—a new sequencing technology based on the “signature” electrical currents generated as a single strand of DNA passes through the nanopore. The…

The more experienced hands in your lab know that molecular biology is rarely just a journey from A to B. As a result, I’ve constructed this short workflow as an introduction to genomic molecular techniques.

Genomic Science has come a long way since the early days of Sanger sequencing in the 1970’s. Today, there are jazzy new sequencing technologies that include fragment analysis, epigenetic sequencing, RNA/transcriptome sequencing and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). Increasingly these technologies are becoming more accessible, but they still require highly specialized (read: expensive) equipment. Unless your…

While it is true that there are some useful websites like SNPedia, or NCBI that can help you find rs codes for genetic variants, sometimes you need that info coming straight from the oven – particularly when you want to look at atypic SNPs or substitutions that have not been validated. So, in this post I…
If you’re new to next gen sequencing, figuring out what to do with your results can be a daunting process. Luckily, you’re not alone—plenty of people have been in your shoes, and there is tons of information about data analysis out there. Here are some free resources you can use to get up to speed…

Next gen sequencing is a powerful technique, one that now lies at the heart of many scientific projects. This power comes with some special challenges, however, and by recognizing them you can ensure that your NGS results are robust. No one wants to publish findings that other scientists fail to replicate, but unfortunately it happens…

“Making the simple complicated is commonplace; making the complicated simple, awesomely simple, that’s creativity.” – Charles Mingus Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technology has boomed in recent years, allowing researchers to probe further into the workings of the genome. According to the theory of simplicity, it is the simple principles on its basis that make…
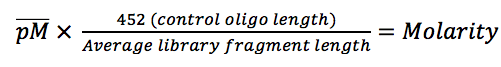
If you want to get the maximum yield and quality from your next-generation sequencing experiment then you are going to need to make sure each of the libraries you produce is carefully quantified ready for pooling and/or loading onto a flow cell. If the quantification goes wrong you’ll get a bad balance of samples within…

Making a Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) library can seem a bit daunting to the new user, as failures can be expensive. But don’t be put off, as NGS library preparation is relatively simple molecular biology, and can be very easy if you choose to use a commercial kit from one of the many suppliers. Take…

The completion of the Human Genome Project in 2003 ushered in a new era of rapid, affordable, and accurate genome analysis—called Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). NGS builds upon “first generation sequencing” technologies to yield accurate and cost-effective sequencing results. Fred Sanger sequenced the first whole DNA genome, the virus phage ?X174, in 1977. In that…

What do these three seemingly disparate studies have in common? After publication, the high-profile findings in each one were questioned due to the presence of batch effects. Batch effects are ever-present and insidious in science, so as researchers we need to always be on guard against them. Keep reading for a run-down of how they…
Size Selection via Gel Electrophoresis Whether you are using NGS for whole genome sequencing, SNP variant analysis, HLA typing, HLA matching, or even transcriptome or miRNA analysis by RNA-seq, size selection is an extremely important consideration for optimum results. Precise size selection can increase sequencing efficiency, save money and improve genome assemblies, as well as…
Thirty-five years ago, Dr. Janet Davison Rowley sat at a microscope in her lab at the University of Chicago and made a remarkable discovery in cancer biology: that leukemia is caused by the translocation of a chromosome. In other words, it is a disease of the DNA. Today, thanks to next generation sequencing (NGS), we can zoom in…

So, you’ve just received a call from the core facility that you hired to prepare and sequence your libraries. The facility director tells you that the sequence data from your next generation sequencing (NGS) experiment does not look good. You panic and, perhaps, let loose a scream of frustration—aaarrrrggghhhh! This project was going to be…

What is HRM Analysis? It is now more than a decade since the introduction of melting analysis to characterize PCR products. Melting analysis following SYBR green-based real-time PCR has become a mainstay in research laboratories worldwide for applications such as gene expression because of it’s ease of design and cost-effectiveness (i.e. no need for expensive labeled probes)….

The eBook with top tips from our Researcher community.