Marketing
Join Us
Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.
Join Us
Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.
Sponsored by:

Sage Science develops sample prep technologies for life science research. We focus on electrophoretic approaches that improve and automate high-value steps in Next Gen sequencing workflows.
Sage sells the Pippin™ line of DNA size selection instruments, which are widely used for DNA, RNA, and ChIP-seq library construction for short-read sequencing. Our systems are also used for preparing high molecular weight DNA for 3rd generation, long-range genomics platforms.
Our products are manufactured at our headquarters in Beverly, Massachusetts, USA.
last updated: March 19, 2025
Share this article:

So, you’ve just received a call from the core facility that you hired to prepare and sequence your libraries. The facility director tells you that the sequence data from your next generation sequencing (NGS) experiment does not look good. You panic and, perhaps, let loose a scream of frustration—aaarrrrggghhhh! This project was going to be…
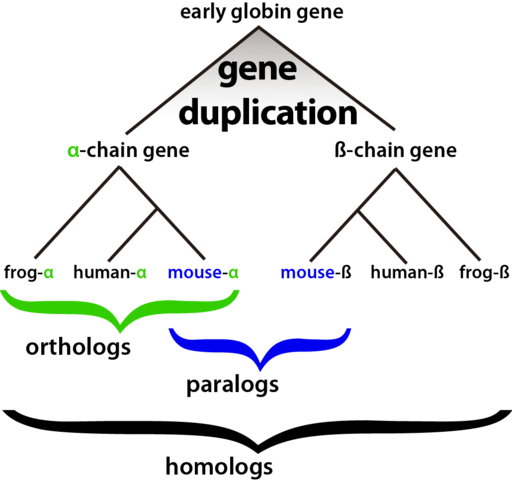
I’ve noticed that there exists some ambiguity about the different terms relating to homology. I’ll try to break them down here, with significant help from Genome Biology.
In biology, a molecular barcode is a characteristic DNA sequence used to distinguish and gather together similar items. Such a simple but powerful concept is useful in various applications. As an example, the Barcoding of Life project aims to identify specimens through the sequencing of standard gene regions, and use these as barcodes. On the other…

Whether your experiment relies upon a reference-based genome assembly or mapping reads to a reference genome to identify variants, you need to choose a human reference genome assembly. But wait! You go to the FTP site of NCBI’s refseq and click on the Homo sapiens folder. There you are presented with two choices. Which one…
It all started with proteins The earliest methods for sequencing were developed for proteins. In 1950, Pehr Edman published a paper demonstrating a label-cleavage method for protein sequencing which was later termed “Edman degradation”. Around the same time Fred Sanger was developing his own labelling and separation method which led to the sequencing of insulin….

CRISPR isn’t just about DNA editing. Discover how you can use Cas13 proteins in your research to knock down, modify or track RNAs in mammalian cells.

The eBook with top tips from our Researcher community.