How to Build Your Own PCR Machine
You can build your own PCR machine using tools and equipment you can get easily and without breaking the bank. Well, what are you waiting for?
Join Us
Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.


You can build your own PCR machine using tools and equipment you can get easily and without breaking the bank. Well, what are you waiting for?

Here’s an easy guide on how to maintain your lab balance. Following these tips will ensure your balance remains clean and perhaps most importantly, accurate.

Are you having problems amplifying GC-rich regions in your PCR reactions? Read this article for 5 easy tips to address these issues!

SAGE, or serial analysis of gene expression, is a technique that enables you to digitally analyze the entire gene expression profile of a cell(s). Before this technique, scientists were limited to studying a few gene’s expression at once by a technique called the expressed sequence tag approach. The coolest part of SAGE is you don’t…

Some techniques can sound very dry but this isn’t one of them! SAGE was first described and published by Velculescu et al. in 1995. At the time, techniques like RNA blotting and expressed sequence tagging were used to study gene expression. However techniques like these were slow and very limited. The speed of SAGE and…
There are some wonderful toys in the lab that enable us to open up a whole new world in science. One of those is a rather pricey and an incredibly sensitive laser-based apparatus capable of counting and sorting cells, detecting biomarkers, and engineering proteins: the flow cytometer. By propelling cells through the path of the…
Predicting how proteins will fold in vivo is a Holy Grail of proteomics and theoretical chemistry. Current hopes are that this can be achieved by designing an in silico platform that can predict protein folding, either de novo (a.k.a. from scratch) or using known proteins as a guide. What would we need to do, why…

How to Obtain a Purer PCR Product and Reduce Non-specific Amplification Unless you’ve gotten your hands on some miraculously specific primers, amplification of only your target sequence without non-specific amplification can be very challenging. Thankfully, a clever and surprisingly simple solution is at hand! A Quick Recap of the Basics In PCR, you design your…

Clinical Trial Coordinator, Clinical Study Coordinator, and Clinical Research Coordinator are all names for the same job and refer to the person responsible for the day-to-day running of human trials. Usually when I tell someone that I’m a Clinical Study Coordinator, they have no idea what that means. I guess it’s like when someone tells…
The first thing you learn about culturing cells is proper aseptic technique and avoiding contamination. After that you’ll learn all the ins and outs of culturing your project’s specific cell line(s). What may not have been covered, is co-culturing, and I don’t just mean ethnic diversity in the lab! Co-culturing is the indirect or direct…
Some viral vectors are the little black dresses of cloning and expression experiments: They work for almost any occasion and always give you the results you were hoping for. Other vectors are more like ballgowns that only come out of storage for special occasions. Let’s wade through all the information out there and take a…
The Boom method, or Boom nucleic acid extraction method, is a solid phase extraction technique for isolating nucleic acids from a solution of biological matter. This is just a fancy way of saying you use this technique to expose and remove the nucleic acids from a cell. First developed by William R. Boom, the Boom…
Extracting protein from tissue samples and cultured cells is Step #1 in many biochemical and analytical techniques. Before you can do a Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE), a Western blot, or mass spectrometry you need to extract your protein. Nowadays, a lot of labs have switched to kits for their protein extraction but these kits can…
We have already looked into the different types of viral expression systems and when you might use one over another in my previous article. But why would you use viral transduction over similar techniques like plasmids? Just a reminder: Transfection is a lab technique where nucleic acids or proteins may be introduced into cells. When…
We’re already gone through the basics of how gel electrophoresis work, compared common gel types like agarose and polyacrylamide and even explored some alternatives. Now let’s look at the native versus denaturing gels. You’ll be a speGEList in no time! Denaturing Gels We’ll start with this one, as it’s very self-explanatory. Denaturing gels are exactly…

Normally you need two primers to amplify your segment of interest – one for the 3′ end of your segment of interest and one for your 5′ end. But if you don’t know the sequence of the regions you’re hoping to amplify this can be a problem! Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE) is a…
Phenol-chloroform extractions and ethanol precipitations can be a royal pain, but here are some tips to help you get tip-top results!

While most may think standard Taq is the backbone of PCR, many other DNA polymerase options exist. The polymerase you use significantly impacts the efficacy of your PCR, specifically on the product yield, the purity of the product, and the faithfulness with which the starting product is transcribed. Sometimes, these matter less, and quick and…

When you share an incubator with a number of people it can be very hard to keep a clean shop and months, or more, of work can be lost due to contamination. The two biggest sources of bugs in an incubator are: Both of these can be kept sterile using a few tips that we’re…
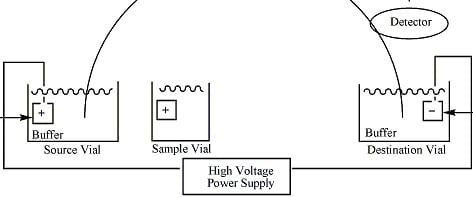
When you think about separating proteins, do you think about separating them using a gel? Specifically using SDS-PAGE? If you answered “yes”, it is for good reason. SDS-PAGE is ubiquitous in molecular biology labs because it is good at separating proteins. However, SDS-PAGE takes a lot of time and is labor-intensive. So let’s expand your…

Traditionally, if you’re hoping to clone a DNA/RNA fragment (or insert) into a vector, such as a BAC you would need: This process looked something like this: cut you vector using exonucleases to expose ends that are complementary to the ends of your insert and then stick your insert into the vector using a ligase….
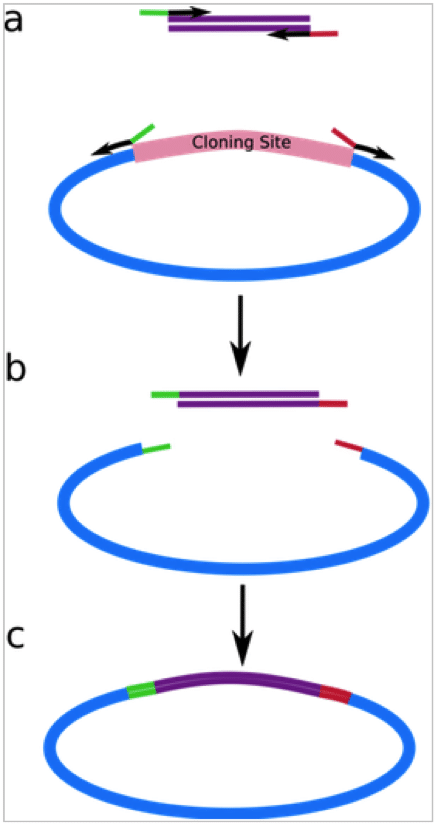
PIPE PCR is a ligase-independent, restriction enzyme-free cloning strategy like SLIC (link to my SLIC article), SLiCE and CPEC. The PIPE method eliminates sequence constraints and reduces cloning and site mutagenesis to a single PCR step followed by product treatment. It is fast, cost-effective and highly efficient. The key step is designing the primers; one…

Science is an expensive business and those who use high energy-demanding techniques may not even realize just how expensive they are. The Cost of PCR Let’s looks at PCR. You need to pay for the machine, all the ingredients including expensive enzymes, a freezer and a fridge for your ingredients, tubes and caps, not to…

There are so many unspoken rules to working in a lab! It’s unnerving what will cause frayed nerves to snap, people not to trust you and a good relationship to turn sour. Here are some of the rules I’ve learned. Feel free to add more in the comments section below. 1. Thou Shalt Not Touch…

Every protocol for single cell PCR can be broken down into two steps. In the first step, the cells are isolated by micromanipulation, laser capture microdissection, flow cytometry, or by direct micropipetting. Next, the genetic material is processed by PCR to amplify your sequence of interest. Here, we’ll go through the different options for isolating…
T cells can be problematic to characterise because they have a wide variety of subtypes and because of the technical difficulties of studying the membrane-bound T cell receptor, but there are situations where you want to be able to do this such as analysing the degree to which immunological memory has been induced to measuring…
When I buy a new sweater, I love finding out that it goes with several pairs of pants, the scarf that’s an awkward color and the earrings I haven’t worn yet. PCR is like this sweater – it goes with almost everything and molecular biology is taking full advantage of this using it at every…
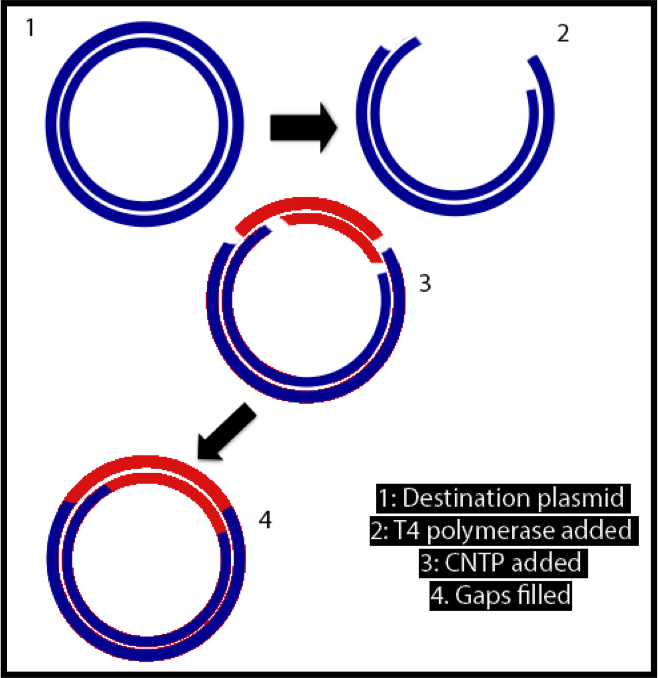
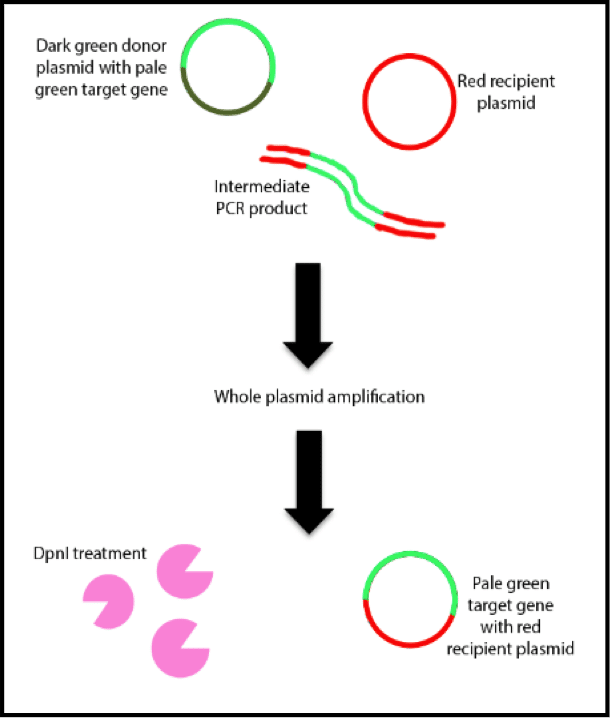
SLIC, or sequence and ligase independent cloning, was developed by Li in 2007 and published in Nature Methods. What makes it a Nature Methods worthy protocol? Unlike other forms of cloning, SLIC does not require restriction enzymes or a ligase! Seriously! Don’t believe me? Why not have a go for yourself? I’ve detailed the main steps below to get you started. How it works To…

What do bunnies, coins and PCR have in common? They all have tails! (ha ha!) Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR or TAIL-PCR is used to sequence and analyse unknown DNA fragments that are adjacent to known sequences. Think of it as being rather like networking. You know you want to get to know someone so you…

You walk into your tissue culture room to find a window open, the incubator’s humidity tray empty and a pipette lying on its side in the hood on a used glove… After you have found and torn to shreds the person responsible for this monstrous act (!!), consider posting the below tips to help those…

A few years ago, I was doing research in a lab in Ireland. Our lab, among many others, was moving to a new building. Everything was chaotic. Half our equipment was in the old building and the new lab was creepishly empty. The fire alarm went off every few days. There was a constant…

Glucose is the preferred food source for E. coli, however when glucose levels drop, E. coli need to look for other ways to feed themselves. One way in which they accomplish this is to replace glucose metabolism with lactose metabolism. The induction and control of lactose metabolism is complicated and its process has been exploited…

The completion of the Human Genome Project in 2003 ushered in a new era of rapid, affordable, and accurate genome analysis—called Next Generation Sequencing (NGS). NGS builds upon “first generation sequencing” technologies to yield accurate and cost-effective sequencing results. Fred Sanger sequenced the first whole DNA genome, the virus phage ?X174, in 1977. In that…

An operon is a functioning unit of genomic DNA that contains a group of genes controlled by a single promoter. Put simply, these genes share information needed to create the tools for a particular task so they share a promoter ensuring they’ll all be transcribed together. The lac, or lactose, operon is found in E….

It’s ironic how much folklore and superstition comes with being in science. “That’s a lucky pipette”, “playing Bach for your cells will help them grow”, “always make your own solutions”; we all have our own tips. Some of them might be well-founded others not so much… Tips from trusted colleagues can be very helpful though….

As with some of the greatest discoveries in science, from penicillin to microwave ovens and play-doh, PCR was discovered serendipitously. Thanks to the work of many scientists, including Watson and Crick, Kornberg, Khorana, Klenow, Kleppe (so many K’s…) and Sanger, all the main ingredients for PCR had been described by 1980. Like butter, flour, eggs,…

It happens to the best of us. You’re minding your own business and suddenly out of nowhere your mastermix is a bubble bath and your primers are enjoying a froth party. Let’s talk about how to deal with these foamy fiends! When you’re making up your mastermix, you could have a variety of ingredients going…

Your stomach clenches. Sweat snakes down your torso. The world seems to slow down. You begin the long, terrifying walk down the corridor. Your mind calls out to you to, “Run! Run now!” but you soldier on until you reach the door and knock. There is no escaping the wrath you will evoke when you…

B.I.T.E., or Bunsen Ill-Treatment and Endangerment, happens every day. In the time since you started reading this article, somewhere out there, a Bunsen burner has been mishandled. This is a dark subject and while some flinch at the thought of discussing it (some stories may be too dark for the public to handle) this writer…
The wide range of applications of PCR has led to an ever-growing list of variants of the technique. While some are optimizations to suit specific requirements and are very similar to basic PCR, others completely turn the technique on its head to formulate novel creative applications in various fields. This article lists some variants of…

The eBook with top tips from our Researcher community.